데이터 사이언스 09 이미지 처리-mahotas
1. 참조
2. 모듈 설치 - mahotas
➜ pip install mahotas
Successfully installed mahotas-1.4.4
3. 경계 찾기
1) 흑백
import mahotas as mh
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
image_raw = mh.imread( './data_science/scene06.jpg' )
plt.figure( figsize=(8, 8) )
plt.imshow(image_raw)
plt.show()

image_grey = mh.colors.rgb2grey( image_raw )
plt.figure( figsize=(8, 8) )
plt.imshow( image_grey )
plt.gray()
plt.show()

thresholding = mh.thresholding.otsu( image )
print( 'Otsu threshold is {}'.format(thresholding))
Otsu threshold is 128
plt.figure( figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow( image_grey>thresholding )
plt.show()

2) 블러링
# 가우시안 블러링
im16 = mh.gaussian_filter( image_grey, 16 )
/home/learn/.pyenv/versions/3.6.2/envs/Jupyter/lib/python3.6/site-packages/mahotas/internal.py:112: FutureWarning: Conversion of the second argument of issubdtype from `float` to `np.floating` is deprecated. In future, it will be treated as `np.float64 == np.dtype(float).type`.
if not np.issubdtype(A.dtype, np.float):
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.imshow(im16)
plt.show()

plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.imshow( im16>thresholding )
plt.show()

4. 초점 맞추기
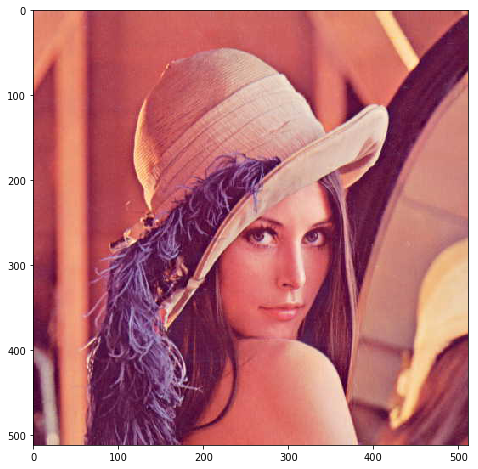
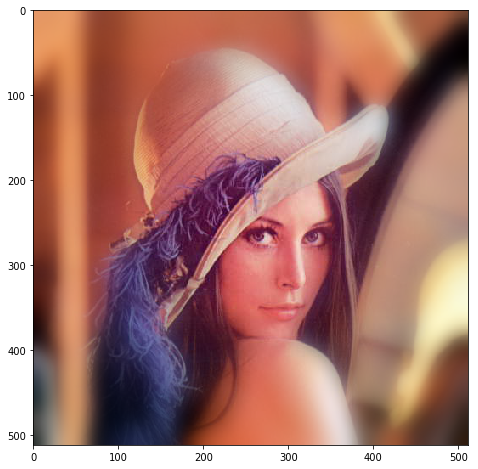
lena_raw = mh.demos.load('lena')
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(lena_raw)
plt.show()

test_transpose_origin = np.array(
[
[ [1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6] ],
[ [7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12] ],
[ [13,14], [15,16], [17,18] ]
]
)
print( test_transpose_origin.shape)
print( test_transpose_origin)
(3, 3, 2)
[[[ 1 2]
[ 3 4]
[ 5 6]]
[[ 7 8]
[ 9 10]
[11 12]]
[[13 14]
[15 16]
[17 18]]]
test_transpose = test_transpose_origin.transpose(2, 0, 1)
print( test_transpose )
[[[ 1 3 5]
[ 7 9 11]
[13 15 17]]
[[ 2 4 6]
[ 8 10 12]
[14 16 18]]]
r, g, b = lena_raw.transpose(2, 0, 1)
r12 = mh.gaussian_filter( r, 12.)
g12 = mh.gaussian_filter( g, 12.)
b12 = mh.gaussian_filter( b, 12.)
im12 = mh.as_rgb(r12, g12, b12)
/home/learn/.pyenv/versions/3.6.2/envs/Jupyter/lib/python3.6/site-packages/mahotas/internal.py:112: FutureWarning: Conversion of the second argument of issubdtype from `float` to `np.floating` is deprecated. In future, it will be treated as `np.float64 == np.dtype(float).type`.
if not np.issubdtype(A.dtype, np.float):
plt.plot( r[0] )
plt.show()
plt.plot( r12[0] )
plt.show()
h, w = r.shape
Y, X = np.mgrid[ :h, :w ]
Y = Y - h/2.
Y = Y / Y.max()
X = X - h/2.
X = X / X.max()
C = np.exp( -2.*( X**2 + Y**2 ) )
C = C - C.min()
C = C / C.ptp()
C.shape
(512, 512)
C = C[:, :, None ]
C.shape
(512, 512, 1)
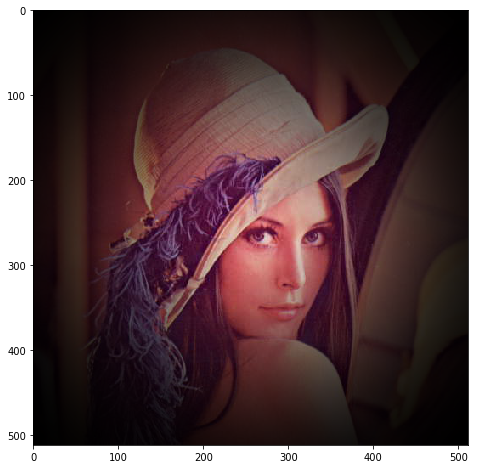
# 중앙 초점
ringed = mh.stretch(lena_raw*C)
plt.figure( figsize=(8,8) )
plt.imshow(ringed)
plt.show()

plt.figure( figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow( im12 )
plt.show()
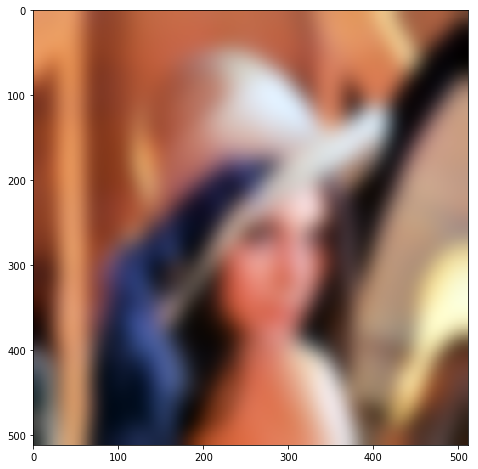

ringed = mh.stretch( (1-C)*im12 )
plt.figure( figsize=(8,8) )
plt.imshow(ringed)
plt.show()
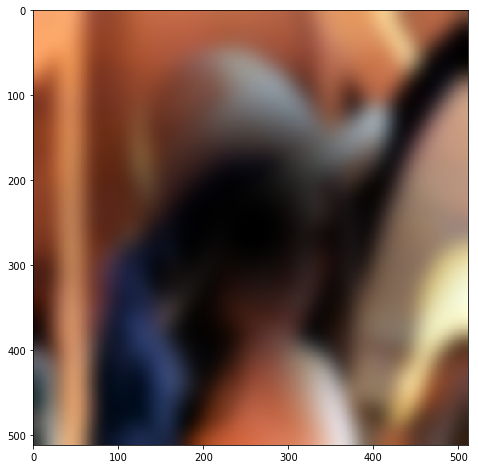

ringed = mh.stretch( lena_raw*C + (1 - C)*im12)
plt.figure( figsize=(8,8) )
plt.imshow(ringed)
plt.show()

5. 이미지 분류
1) scikit-learn 설치
➜ pip install -U scikit-learn
Installing collected packages: scikit-learn
Successfully installed scikit-learn-0.19.1
2) 이미지 모음
from glob import glob
images = glob('./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/*.jpg')
images[:5]
['./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/text14.jpg',
'./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/building04.jpg',
'./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/scene04.jpg',
'./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/scene05.jpg',
'./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/text24.jpg']
images[0][ len("./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/") : - len('00.jpg')]
'text'
im = mh.imread( images[0] )
im = mh.colors.rgb2gray( im, dtype=np.uint8)
3) 이미지 특성(haralick 방법)과 라벨을 추출
features = []
labels = []
for im in images:
labels.append( im[ len("./data_science/SimpleImageDataset/") : - len('00.jpg')] )
im = mh.imread(im)
im = mh.colors.rgb2gray( im, dtype=np.uint8 )
features.append( mh.features.haralick(im).ravel() )
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# from sklearn import cross_validation
from sklearn import model_selection
clf = Pipeline(
[
( 'preproc', StandardScaler()),
( 'classifier', LogisticRegression() )
]
)
cv = model_selection.LeaveOneOut( )
cv.get_n_splits( images )
90
scores = model_selection.cross_val_score( clf, features, labels, cv=cv )
scores
array([1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1.,
1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0.,
1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 0., 1.])
print( 'Accuracy: {: .2%}'.format( scores.mean() ) )
Accuracy: 81.11%
def chist(im):
"""Compute color histograms of input image
Parameters
----------------------
im : ndarray
should be an RGB image
Returns
---------------
c : ndarray
1-D array of histogram values
"""
# Downsample pixel values
im = im//64
# We can also implement the following by using np.histogramdd
# im = im.reshape((-1, 3))
# bins = [ np.arange(5), np.arange(5), np.arange(5) ]
# hist = np.histogramdd( im, bins=bins )[0]
# hist = hist.ravel()
# Separate RGB channels
r, g, b = im.transpose( (2, 0, 1) )
pixels = 1*r + 4*g + 16*b
hist = np.bincount( pixels.ravel(), minlength=64 )
hist = hist.astype(float)
return np.log1p(hist)
features = []
for im in images:
image = mh.imread(im)
features.append( chist(image) )
scores = model_selection.cross_val_score( clf, features, labels, cv=cv )
print( 'Accuracy: {: .2%}'.format( scores.mean() ) )
Accuracy: 91.11%
# 모든 속성을 반영
features = []
for im in images:
imcolor = mh.imread(im)
im = mh.colors.rgb2gray( imcolor, dtype=np.uint8 )
features.append(
np.concatenate(
[ mh.features.haralick(im).ravel(), chist(imcolor), ]
)
)
scores = model_selection.cross_val_score( clf, features, labels, cv=cv )
print( 'Accuracy: {: .2%}'.format( scores.mean() ) )
Accuracy: 96.67%
4) 유사 이미지 찾기
features = []
for im in images:
imcolor = mh.imread(im)
# Ignore everything in the 200 pixels close to the border
imcolor = imcolor[200:-200, 200:-200]
im = mh.colors.rgb2gray( imcolor, dtype=np.uint8 )
features.append(
np.concatenate(
[ mh.features.haralick(im).ravel(), chist(imcolor), ]
)
)
sc = StandardScaler()
features = sc.fit_transform(features)
from scipy.spatial import distance
dists = distance.squareform( distance.pdist( features ) )
def selectImage( n, m, dists, images):
image_position = dists[n].argsort()[m]
image = mh.imread( images[image_position] )
return image
def plotImages(n):
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15))
plt.subplot(141)
plt.imshow( selectImage(n, 0, dists, images) )
plt.title('Original')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(142)
plt.imshow( selectImage(n, 1, dists, images) )
plt.title('1st similar one')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(143)
plt.imshow( selectImage(n, 2, dists, images) )
plt.title('2nd similar one')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(144)
plt.imshow( selectImage(n, 0, dists, images) )
plt.title('3rd similar one')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
plotImages(0)

plotImages(1)

plotImages(11)

plotImages(31)

plotImages(61)
